Views: 11 Author: Monica Publish Time: 2025-10-20 Origin: Site








Stainless steel pipes are widely used in industries such as petrochemicals, aerospace, semiconductors, food, and medicine due to their corrosion resistance, high strength, and long life.
This article will introduce the making of stainless steel pipes, providing an in-depth understanding of each step in their production.
The making process of stainless steel pipes is divided into two types: seamless pipe manufacturing and welded pipe manufacturing, which differ in raw materials and forming methods.
Seamless pipes are primarily used in applications requiring high pressure, high temperature, high strength, and stringent corrosion resistance.
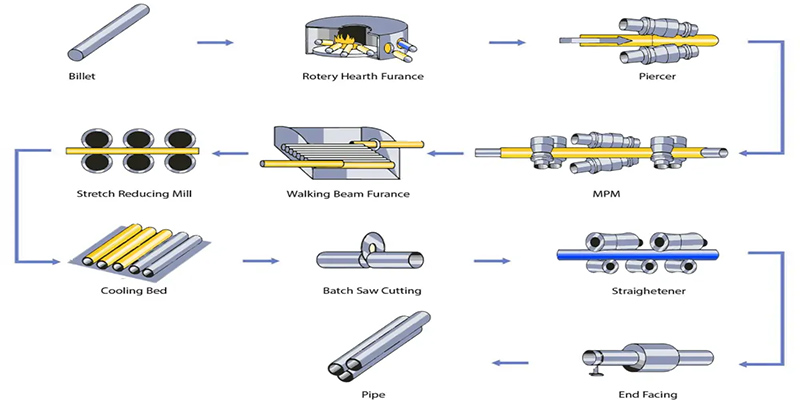
1. Raw Material Preparation & Billet Heating
Jinie selects high-quality round steel billets that meet specific chemical composition requirements, such as grades 304 and 316L. The billets undergo surface inspection and treatment to remove surface defects. They are then heated to their thermoplastic temperature in a ring-shaped or pusher-type heating furnace in preparation for piercing.
2. Piercing
This is a key step in seamless pipe manufacturing. The heated round billet is fed into the piercing mill. Two rolls rotating in the same direction and at an angle push the billet forward while rotating. A centering drill drills the billet through the center, creating a hollow bloom.
3. Hot Rolling & Elongation
The hollow bloom then enters the pipe rolling mill. Through multiple rolling passes, the outer diameter and wall thickness of the rough tube are reduced and stretched by the combined action of external rollers and an internal mandrel, gradually approaching the finished product specifications while improving the internal structure.
4. Sizing & Reducing
Before or after cooling, the rolled tube passes through multiple mandrelless reducing mills or stretch reducing mills to further precisely control and adjust the outer diameter, roundness, and wall thickness, bringing it to the final dimensions within the required drawing tolerances, preparing it for subsequent cold working.

5. Cold Drawing or Cold Rolling
Cold working is required for tubes requiring higher dimensional accuracy, thinner wall thickness, or superior surface quality. Cold drawing involves pulling the tube through a die smaller than its diameter; cold rolling involves rolling the tube using rollers on a cold rolling mill. Cold working significantly improves the surface finish and mechanical properties of the tube, but it can also introduce internal stresses.
6. Solution Annealing & Straightening
Cold working and hot rolling processes induce work hardening and residual stresses in the pipe, potentially leading to the precipitation of harmful carbides. Therefore, the pipe must be heated to the austenitizing temperature and then rapidly cooled. Solution annealing eliminates internal stresses, restores plasticity, and dissolves carbides, ensuring optimal corrosion resistance. The pipe then passes through a straightener to remove bends.
7. Pickling, Passivation, and Surface Finishing
After heat treatment, a layer of scale forms on the pipe surface, which must be removed by pickling. Subsequently, passivation or natural passivation forms a dense, stable chromium-rich oxide film on the pipe surface, which fundamentally protects the stainless steel's corrosion resistance. Finally, polishing, lapping, and other finishing processes are performed according to customer specifications.
Welded pipes are primarily used in low- and medium-pressure fluid transportation, structural support, and decorative applications, featuring low production costs and high production speeds.
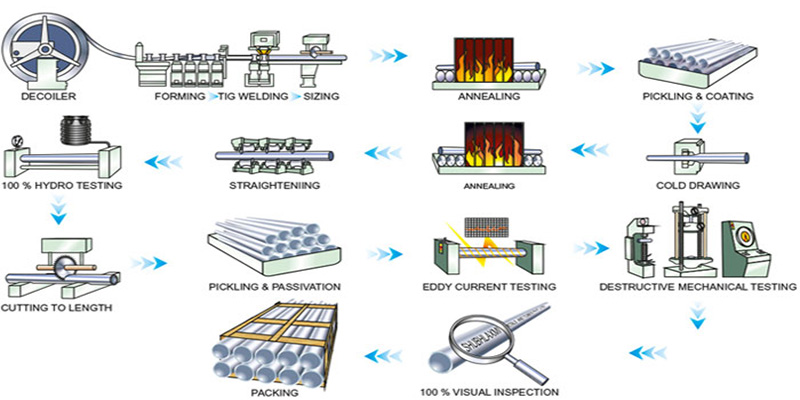
1. Strip Preparation & Slitting
Qualified stainless steel coils are used as raw material. The coils are first uncoiled and flattened, then precisely cut into narrow strips of a specific width using a slitter. The width of the strip determines the outer diameter of the final welded pipe.
2. Forming
The strip passes through a series of forming rollers, which gradually coil and bend the flat strip until its edges meet to form an open-seamed round tube.
3. Welding
The formed open-seamed tube enters the welding zone, where a suitable welding method is used to fuse the tube seam. For stainless steel pipes, TIG/GTAW, plasma welding, or laser welding are primarily used to ensure high-quality welds and minimize heat-affected zones. During the welding process, external and/or internal weld seams are typically scraped to remove excess weld metal.

4. Sizing & Shaping
The welded pipe enters the sizing unit, where it passes through multiple sizing rollers to compress and straighten the pipe to ensure that its outer diameter, roundness, and wall thickness meet precise tolerances.
5. Eddy Current/Ultrasonic Testing
After sizing, the weld seam is typically subjected to in-line nondestructive testing (NDT), such as eddy current testing for surface and subsurface defects or ultrasonic testing for internal defects, to ensure real-time weld quality assurance.
6. Heat Treatment, Pickling, Passivation, and Straightening
Similar to seamless pipe, welded pipe typically undergoes in-line solution annealing to eliminate weld stress and structural inhomogeneities and restore corrosion resistance. This is followed by pickling, passivation, and straightening.
Whether seamless or welded, the final product undergoes rigorous quality control.

Mechanical & Chemical Testing
Tensile tests, flattening tests, flaring tests, and hardness tests are performed to verify that the mechanical properties of the pipes meet standard requirements. A spectrometer is also used to verify the chemical composition of the pipes.
Hydrostatic/Pneumatic Testing
Hydraulic or pneumatic pressure tests are performed on the pipes at specified pressures to verify their pressure resistance and leak-proof properties.
Dimensional & Visual Inspection
Using specialized measuring tools, the pipes' outer diameter, wall thickness, length, curvature, and other dimensions are precisely measured. The surface is then inspected for defects such as cracks and scratches.

Marking & Packaging
In accordance with standard requirements or customer specifications, information such as steel grade, heat batch number, dimensions, and standard are printed or marked on the pipes. Finally, the pipes are packaged professionally to prevent moisture and impact and are ready for shipment.
The manufacturing process of stainless steel pipe is a complex and precise process involving multiple key steps and technologies. JN ensures the high quality and reliability of each stainless steel pipe you produce through premium material selection, advanced processing technology and strict quality control.
JN Special Alloy Technology Co., Ltd. is a leading stainless steel pipe manufacturer and supplier in China. We offer stainless steel, duplex steel, super duplex steel, and nickel alloy steel pipes. Every pipe produced by JN conforms to ASTM standards, and we accept custom sizes and flexible MOQs.
JN provides first-class customer service, available 24/7, especially for time-sensitive orders. From receiving your inquiry, providing a quote, signing the contract, paying the deposit, arranging production, packaging and shipping, to receiving the goods, we assign a sales representative to provide you with one-on-one service.
Throughout the entire ordering process, we are committed to ensuring your satisfaction.
Contact us now for the latest steel pipe quote!